GLOBAL STRATEGY : ANALYSIS AND PRACTICE
(Using the tools and models of Strategic analysis account for the relative success of the company)
INTRODUCTION
Since its beginning 1938 with a small business of export in Korea (Taegu), Samsung has grown-up among the leading electronics companies of the world, focusing in digital appliances & media, memory, system integration and semiconductors. Currently innovative and highest quality products and processes of Samsung’s are recognized throughout the world. Such timeline denotes the key highlights in history, showing of Samsung how this company extended its lines of product and spread, increased its revenue besides market share, and then has followed company’s mission of creating better life for customers around the world (Samsung, 2012a).
Source: Samsung (2012a)
As part of such vision, Samsung could map out a definite strategy to reach $400 billion in returns as well as become one of the topmost five brands in the world by 2020. For this, Samsung has too built three strategic management tools: Creativity, Partnership, as well as Talent. Samsung is motivated regarding future growth. As the company’ earlier endeavors to search new places, comprising health, medicine, as well as biotechnology. A dedication has been observed by Samsung to remain creative leader in new markets as well as performing a really No. 1 business moving ahead (Samsung, 2012a).
Source: Samsung (2012a)
The digital era has conveyed revolutionary shift and prospect of global business, and Samsung made a response with advanced technologies, competitive products, as well as continuous innovation (Samsung, 2012b).
During 1998, Samsung’ chairperson planned that global strategy of the brand and low-end items of Samsung could be moved out from the super market of North America. Samsung implemented a related brand strategy in Chinese market. Mobile handset of Samsung is having superior features like its miniaturization, lightweight, as well as power-saving facilities. It has good image of the product like major advantage of technology, great quality as well as innovative design, through a base for vast the competition in Chinese market. Thus, resources of marketing which Samsung gathered in Korea, Europe and the US have been transported to China as well as have been utilized to build brand strategy (Lin, 2007).
Since more than 70 years, devotion has been made by Samsung to make a better world by diversified business that currently span advanced technology, skyscraper & plant construction, medicine, semiconductors, petrochemicals, , finance, hotels, fashion and more. Flagship company of Samsung i.e. Samsung Electronics is leading the global market in manufacturing of advanced electronics as well as digital media. With the innovative, dependable products & services; talented staffs; an accountable method towards business as well as worldwide citizenship; then collaboration with partners and consumers, the world is taken by Samsung towards an imaginative new way (Samsung, 2012c).
Strategic management
Although the huge attention in strategy as well as the numerous points through that this is observed, such methods do not appear to give enough knowledge of considerate of strategic management procedure in practice. It could be however partially because of the domination of modernist outlook, making a tool in which direction is controlled, while strategy decides structure besides in which the plan defines actuality (Clegg et al., 2004).
Porter’s Five Forces Model
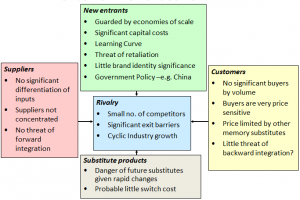
The core of building a strategy is connecting an organization with its environment. Thus the stage of this study is critical to the result of overall planning procedure. A key segment of the study is an analysis of external environment. Several tools as well as methods have been established to help strategic planners to evaluate external environment. The main interest is evaluating potentiality of the profit in industry. Competitive Forces Model of Michael Porter (generally stated as Porter’s Five Forces Model) is definitely the most extensively utilized outline for profit potentiality in the industry. The combined power is termed as five forces (see figure 1) vary from industry to industry. Every such five forces are reliant upon structural dimensions that collectively influence profit prospective. Entire five forces equally decide the strength of the profitability and competition in the industry. The forces that are the strongest remain crucial from viewpoint of formulating strategy (Porter, 2008).
Figure 1 : Porter’s Five Forces Model of Samsung
Source: Porter (2008)
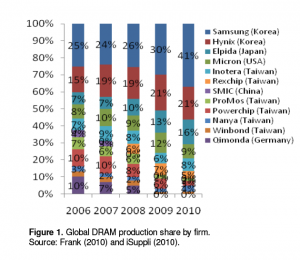
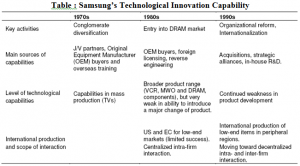
During its initial phases of expansion, Samsung Electronics Company (SEC) was not having appropriate technologies and technical talents. Several US as well as Japanese organizations rejected transferring technology to Samsung, as it was depending on overseas technologies. Initial strategy of Samsung was “imitation” integration, transformation, acquisition as well as use of products as well as procedures through the US as well as Japanese companies. During that time, it was not clear as well as could not be expected that a company like Samsung which typically depend on imported overseas technology, with mediocre products, with low prices, and low quality plus design could be one of the leading companies of the world in electronics market. It was also not expected that it can be a challenge for competing with such organization that when denied Samsung to share as well as provide technology. Samsung not only could catch up, however also exceeded several top DRAM manufacturing organizations like Toshiba, IBM, Motorola and Micron in the global market. Above a decade, this sustained to remain No.1in industry ranking for DRAM market holding the highest share of 41% in the market during 2010 as displayed in Figure 2.
Figure 2: Global DRM production share by firm
Source: Frank (2010)
Samsung Electronics could emerge like a largest maker of memory chip in the world having a topmost position in DRAM as well as NAND flash markets. Strategic management by leveraging resources as well as competences allow an organization’s entry into new market domains through resource sharing and applying it to new application (Danneels, 2010).
In context of Samsung, resource as well as competency power might be observed in its effective strategy of diversification into flash memory as well as TFT-LCD. In spite of the higher threat and fluctuating condition in memory business, Samsung aggressively, made continued investment in R&D as well as production facilities. Growing development cost of every group of DRAM products has been observed. Heavy investment was made by Samsung during economic recessions while other rivals were decreasing their investment, and acquired significant profits while industry faced an increase in demand. (Samsung Electronics, 2010).
Park et al. (2008) stated that during 1998, only three years when it begun TFT-LCD business, Samsung obtained the biggest market share of the world, presenting innovative products ahead of Japan. From then it sustained its leadership in the world. Samsung’s technological strategy focus in DRAM as well as major human resources was transported to TFT-LCD business. Specifically, R&D ability and funding, management of operations and systems of quality control, choice of strategic investment know-how as well as the capacity to establish and achieve a skilled staff were entirely shifted from business of semiconductor to TFT-LCD, resulted in considerable synergies (Park et al., 2008).
Chen (2005) explained six techniques for effective TICs i. e. Technological Innovation Capabilities, for instance, the foremost role of companies, technology innovation (TI) strategy, technology as well as research centers, TI environment and TI resources upgrading motivation for TI of the entrepreneurs. Chen (2005) too proposed other total innovation management (TIM) strategic like a foundation towards indigenous technology innovation strategy. The aim and objective of total innovation management strategy is nurturing core competency besides augment core competitive abilities having strategy like a way and technology innovation as fundamental. It syndicates and synchronizes organizational strategic management, culture, market as well as institutional innovations (Xu, 2005).
Though such models and structures give valuable method for understanding technological innovation developing nations, maximum of them too indicate existing states of technology innovation capabilities environment. It has reconsidered Korean’s model of strategic innovation management. He observed that innovation model of Korea developed was by three phases: 1) collective learning, 2) collection recombination as well as 3) collective creativity. These three stages are called “collective creation” that may relate to Kim’s (1997 three-stage model. Author’s study has recommended an exploration for a new strategic analysis model (Choi, 2010).
Source: Choi (2010).
THE SPIRAL PROCESS STRATEGIC TOOL OF TECHNOLOGICAL INNOVATION
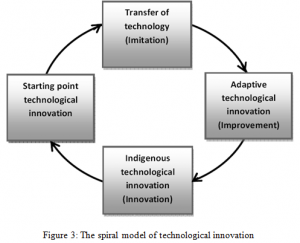
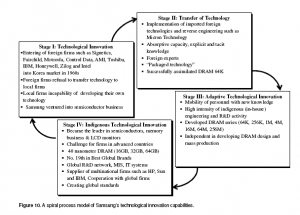
A strategic management model i.e. spiral process of technological innovation proposed by Ali and Park (2010). In this model four stages are there that are: 1. Technological Innovation, 2. Transfer of Technology, 3. Adaptive technological innovation as well as lastly, 4. Indigenous Technological Innovation. Majority of them are built by the spiral procedure as depicted in Figure 3.
Source : Salimuddin (2004)
Samsung could effectively enter to such phase of technological innovation. The company started DRAM technology in first phase. In second phase is it attained “transfer of technology”. Organizations of developing nations import technology from foreign that is commonly called as transfer of technology as well as also international transfer of technology. Big multinational companies are the main origins of such technology. Because of reliance of other different phases, this phase gets critical. Several receiving nations have no thorough knowledge of their technology requirement. Such companies are not only requiring the skill to recognize the suitable technology however also a careful implication regarding the necessity of technology for solving their difficulties (Salimuddin, 2004).
In spite of its absence in technological capability in semiconductors, it was possible for Samsung to develop its competency quickly by external acquisition as well as integration of technologies through multiple sources. Samsung’s global strategic plans used several modes like joint ventures, technology licensing, acquisitions, overseas R&D centers, equipment suppliers, as well as part-time consultants for accessing rapidly and adopt technologies (Shin and Chang, 2003).
Attaining synergy as well as a competitive advantage can be a purpose why companies enter into a strategic alliance. Instead of entering to a market alone, making a strategic alliance gives a process to reduce risk of new market, intercontinental expansion, research and development etc. (Soares, 2007).
GLOBAL PROCUREMENT OF SAMSUNG
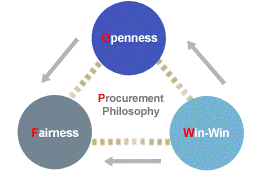
Samsung Electronics as well as Suppliers would co-operate to achieve top performance at Global Top Tier depending on “Win-Win” philosophy of co-existence as well as co-prosperity amid Samsung Electronics and its esteemed Suppliers (Samsung, 2012c).
Figure : Samsung’s Strategic Model of Global Suppliers
Being leader of digital technology in the world, Samsung Electronics is succeeding towards a new age of product development, corporate culture besides contributing towards global society. For achieving it goals, they understand how significant is building associations as well as have total support through high class suppliers (Samsung, 2012c).
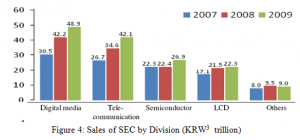
Samsung Electronics could grow to be among the world’s biggest electronics company having revenue of US$ 119.1 billion as well as an operating profit of US$ 9,920 million. This is the first company in Korea which surpassed KRW100 trillion in sales as well as KRW10 trillion in net income. Samsung has accomplished a remarkable share in domestic market and also in global market. During 2005, Samsung could exceed its Japanese competitor (Sony) by remaining biggest consumer Electronics Company in the world that was rated nineteenth in Best Global Brands of Interbrand during 2009 (Samsung, 2010). During 2007, it exceeded Motorola by remaining the second biggest mobile phone manufacturer in the world, whereas it remained largest technology company of the world in 2009 by surpassing Hewlett-Packard- HP (USA) and Siemens (Germany) with US$125 billion in global sales globally. Profits for Samsung come through four major businesses, displayed in Figure 4 (Samsung, 2010).
Source: Samsung (2010)
Considering the situation of Samsung, when MNC companies declined sharing their technology with them, it essentially started technological innovation of Samsung. Samsung established its technological competency through reverse engineering as well as by transfer of technology. It executed, collected and created innovative imported technology showed in Figure 10 (Samsung, 2010).
Source: Samsung (2010)
The hallmarks of leadership of Samsung are creativity, collaboration as well as excellence. World’s utmost talented managers are attracted as well as constantly company’s culture is evolved for supporting them to foster innovative ideas that is advance technology, new products as well as markets to improve the daily lives of its customers (Samsung, 2012d)
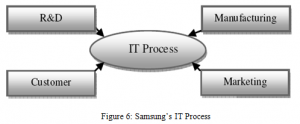
Currently, fast response of Samsung’s towards any type of environmental variation, in every segment of of strategic management practice like managing administration, managing customer, R&D management and supply change management is combined through the process of information technology (IT) as presented in Figure 12 (SEC, 2010).
Source: SEC (2010)
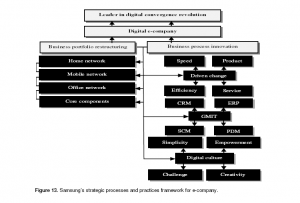
At present, Samsung is major in revolution digital convergence having its strength in becoming a digital e-company through making advanced digital products as well as e-processes (SEC, 2010). Samsung’s future strategy is to gather cutting-edge technologies besides core competencies as well as endeavoring to re-appear like an e-company of world class that would lead revolutions of digital convergence. The company is concentrating on and developing innovative strategies for mobile network, office network and home network core components for achieving its product innovation strategy, depicted in Figure 13 (SEC, 2010).
Source: SEC (2010)
GLOBALIZATION STRATEGY AND NETWORK OF SAMSUNG
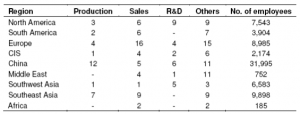
Globalization was extended after 1994 by Samsung once its strategic management introduced the new management drive in 1993 (Chang, 2008). Currently, the company is having nearly196 subsidiaries comprising, sales 53, manufacture 39, R&D centers 24 as well as other 80 centers (comprising supply hubs, branch offices and design centers etc.) as well as 61 centers for R&D in 61 nations as presented in Table 7. Presently Samsung is following strategic alliances in forward-looking companies from abroad about cooperation in technology, standardization, marketing as well as supplier parts. The company is seeking strategic alliances with top organizations in LCD monitors, semiconductors, DRAMs, high speed memory as well as CDMA mobiles (SEC, 2012).
Table : Samsung Global Network
Source: SEC (2010)
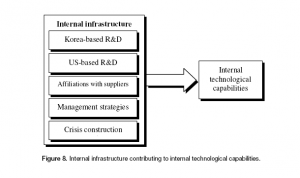
Since Samsung is a late beginner, in the starting Samsung dependent on borrowed technologies, however aggressively it invested in time, concentrated on technologies having obvious routes (Chang, 2008), it followed the strategies of late comers as mentioned in Figure 7 as well as internal infrastructure that depicted in Figure 8.
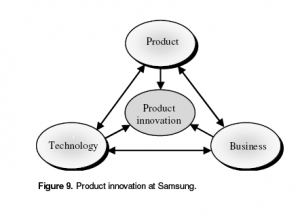
These are aspects of global strategic management which made contribution to success of Samsung. Strong global Research and Development strategy of Samsung, effective incorporation of process as well as innovation in production as displayed in Figure 9, achievement in DRAM development, product portfolio as well as solution, efficacy in production, cost efficiency as well as rapidity are the initial competitive advantages which created it go ahead in the industry.
Source: SEC (2010)
CONCLUSION
From the above global strategic management models it can be understood that the core of building a strategy is connecting an organization with its environment. Several tools as well as methods have been established to help strategic planners to evaluate external environment. The main interest is evaluating potentiality of the profit in industry. Being a late beginner Samsung was dependent on borrowed technologies initially that gave a threat to the company in global markets, however it aggressively invested in time, concentrated on technologies having obvious way. Samsung made a definite strategy to reach $400 billion to become one of the topmost five brands in the world by 2020. For this, Samsung has built three strategic management tools: Creativity, Partnership, as well as Talent. In spite of the higher threat and fluctuating condition in memory business, Samsung aggressively, made continued investment in R&D as well as production facilities. Heavy investment was made by Samsung during economic recessions while other rivals were decreasing their investment, and acquired significant profits while industry faced an increase in demand. Samsung could acquire a remarkable share in domestic market and also in global market; Samsung could exceed its Japanese competitor (Sony) by remaining biggest consumer Electronics Company in the world in 2005. The hallmarks of leadership for Samsung are creativity, collaboration as well as excellence. By appointing world’s best talented managers and supporting them to foster innovative ideas that is advance technology, new products as well as markets to improve the daily lives of its customers. These are aspects of global strategic management which made contribution to success of Samsung.
REFERENCES
Ali M, Park K (2010). The Spiral Model of Indigenous Technological Innovation Capabilities for Developing Countries. Empirical Studies in Social Sciences – 6th International Student Conference, Turkey, April 14-15, 2010, Izmir University of Economics, Izmir.
Chang Sea-Jin (2008), Sony vs. Samsung: the inside story of the electronics giants’ battle for global Supremacy Hoboken, John Wiley and Sons, NJ.
Chen Jin (2005) “Towards Indigenous Innovation: Pathways for Chinese Firms” The presentation at Workshop of “Technology Innovation and Economic Development”, May 25-27th, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China.
Choi Y (2010), “Korean Innovation Model, Revisited”, STI Policy Review, 1, 1, pp.93-109.
Clegg, S., Carter, C. and Kornberger, M. (2004), “Get up, I feel like being a strategy machine”, European Management Review, 1, pp.21-28.
Danneels E. (2010), “Trying to Become a Different Type of Company: Dynamic Capability at Smith Corona”, Strategic Management Journal, 32, pp.1-31.
Frank WAY (2010), DRAM Market Outlook. SEMICON Taiwan 2010 GSA Memory Conference, Taiwan, Sept, Morgan Stanley Research
Lin, H. (2007), “Chapter 5: Marketing-Resources Based Competition: Strategies for the Catch-up of South Korean Firms, the Latecomers in the Chinese Market”, Sato&Kawakami eds., Competition and Cooperation among Asian Enterprises in China, Chosakenkyu-Hokokusho, IDE-JETRO.
Park T.Y., Choung, J.Y. and Min, H.G. (2008), “The Cross-industry Spillover of Technological Capability: Korea’s DRAM and TFT-LCD Industries”, World Development, 36, 12, pp.2855-2873.
Porter, M.E. (2008) “The Five Competitive Forces That Shape Strategy”, Harvard Business Review, January 2008, pp. 79–93.
Salimuddin, M. (2004), “Technology Management-Issues & Strategy for Developing Countries” Presented in ICQI’S 8 th Int’l Convention on Quality Improvement, in Lahore Aug 21-22, 2004.
Samsung (2010), “The New ‘Big Blue'”, The Korea Times, January 29.
Samsung Electronics (2010). Samsung Electronics 40-year History(in Korean), Seoul, Korea
Shin, Jang-Sue and Ha-Joon, Chang (2003), Restructuring Korea Inc., Routledge, London.
Xu Q (2005) “TIM-Based Indigenous Innovation :Best Practice of Haier & other Manufacturers” The presentation at the First Forum on Global Manufacturing and China, Hang Zhou, Zhejiang ,China.
Web sources
Bernadette, S. (2007), “The use of strategic alliances as an instrument for rapid growth, by New Zealand based questor companies”. [Online] viewed on 9th August, 2012 from http://unitec.researchbank.ac.nz/handle/10652/1251
Samsung (2012a), “Vision 2020”. [Online] viewed on 10th August, 2012 from http://www.samsung.com/in/aboutsamsung/corporateprofile/vision.html
Samsung (2012b), “Samsung’s History”. [Online] viewed on 10th August, 2012 from http://www.samsung.com/in/aboutsamsung/corporateprofile/history.html
Samsung (2012c), “About Samsung”. [Online] viewed on 9th August, 2012 from http://www.samsung.com/in/aboutsamsung/
Samsung (2012c), “Global Procurement: Looking for Potential Suppliers to lead the Future with Samsung Electronics”. [online] viewed on 10th August, 2012 from http://www.samsung.com/in/aboutsamsung/globalprocurement/globalprocurement.html
Samsung (2012d), “Management”. [Online] viewed on 10th August, 2012 from http://www.samsung.com/in/aboutsamsung/management/index.html
SEC – Samsung Electronics (2012), “2012 Sustainability Report – Global Harmony with people, society & environment”. [Online] viewed on 10th August, 2012 from http://www.samsung.com/us/aboutsamsung/sustainability/sustainabilityreports/download/2012/2012_sustainability_rpt.pdf
SEC (2010), “2009-2010 Sustainability Report”.[Online] viewed on 10th August, 2012 from http://isaonline.org/documents/Annual_Reports/Annual_report_2009-10.pdf